Note 6 Processing instruction, structured input/output
(Last updated: 9/25/2024)
1. Drills and some research findings in SLA
1.1 Type of drills/exercises in classroom
Mechanical => meaningful => communicative
Mechanical: No information is exchanged. Grammar drill
I drove the car to campus. => The car was driven to campus by me.
Meaningful: Information is exchanged, but it is not new/unknown before. It is not focused on grammar.
Q: (Looking at the sky outside) How is the weather today?
A: It's clear/sunny.Q: (Class in an afternoon) Is it raining right now?
A: No.
Communicative: New information is provided. No focus on grammar.
Q: (Coming into the classroom looking for a book) Where is my book?
A: The book was sent to the Lost and Found (yesterday).
1.2 Some research findings in SLA
1.2.1 Acquisition order
- Acquisition order vs. instruction order
e.g., Compare the sequence of grammar in the textbook vs. errors made by learners - Natural order of acquisition
In English, for example, one-word --> two-word --> multi-word stage --> Y/N question --> WH question --> Subjunctive
1.2.2 Input and intake
Input --> intake --> developing system --> output
|
Processing mechanisms
|
Focused practice
- Input: What is provided to learners
- Intake: The linguistic data in the input that learners attend to and hold in working memory
1.3 Input processing and VanPatten's principles
1.3.1 Input processing
Psycholinguistic strategies and mechanisms by which learners derive intake from input.
1.3.2 VanPatten's Princiles
- The primacy of meaning principle (c.f., p139)
- Content before anything else
- Lexical items before functional words/grammatical forms
- Teacher give me book. vs The teacher gives me a book.
- No redundancy of grammar forms
- She walked to school yesterday. vs She walk to school yesterday.
- Meaningful grammar forms over others irrespective of redundancy
- I had eaten dinner before you arrived.
- I ate dinner before you arrived.
- Availability of resources: Limited capacity of human brain at a given time
- Sentence location, i.e., initial before other positions
- I wouldn't do it if I were you. vs If I were you, I wouldn't do it.
- The first noun principle: It is more likely taken as the subject or
agent
- John hit Mary
- Mary was hit by John
- Video clips:
1.3.3 Examples
1) Zuotian xiayu, jintian mei xiayu.
Yesterday rain, today not rain
It rained yesterday (but) not today.2) Wo zuotian kan shu, baozhi mei kan.
I yesterday read book, newspaper not read
I read book yesterday, ...
2. Processing instruction and structured input
2.1 Processing instruction
- Given information about a structure or form
- Informed of a particular processing strategy that may negatively affect their picking up the form or structure during comprehension, i.e., We intend to influence, alter or improve the way learners process input
- Are pushed to process the form or structure during activities with structured input, i.e., get learners' attention through input manipulated in particular ways
Example
- Target form: English 3rd person singular 's
- What are the processing problems?
- Lexical Preference Principle. Compare
Johnny likes Big Mac.
vs.
Johnny like Big Mac.
- Lexical Preference Principle. Compare
2.2 Input enhancement
- Input flooding: Lots of instances of the same grammatical form
- Text (i.e., connected sentences) enhancement: Instances of the same category
- Recast: Present the same material in different ways (e.g., oral and written) and forms (e.g., active vs. passive)
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LIAhI5oEgHE
2.2 Types of activities for structured input
- Referential: Right or wrong
- Affective: Students' opinionated responses
Task-based categorization
- Binary options
- Ordering and ranking
- Selecting alternatives
- Matching
- Surveys
- Supplying information
Examples
1) Who best fits the desciption
Instructon: Listen to the following statements and decide which character from the Simpsons best fits the description.
Homer Lisa Bart and Lisa"Who works hard at school?" (Answer: Lisa)
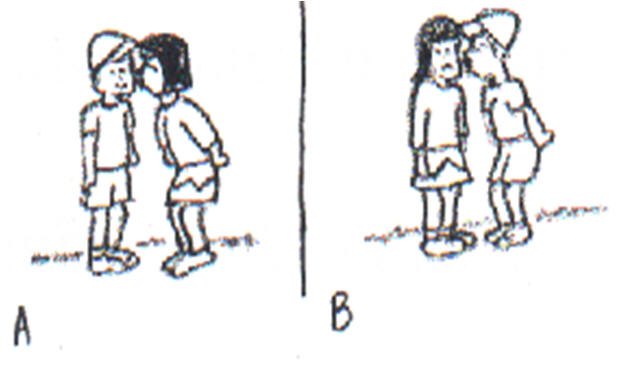
2) Objective pronoun
Who kisses whom: He kisses her/She kisses him.
3) Reflexives
George is vain. He always looks at _______.
1) him in the mirror.
2) himself in the mirror.Susan is unselfish. She always helps __________.
1) others in times of need.
2) herself in times of need.
2.3 Guidelines for developing structured input activities
- Present one thing at a time
e.g., Keep it short and use one form - Keep meaning in focus
i.e., The activity requires comprehension - Move from sentence to connected discourse
e.g., in sequence, and/or logical order - Use both oral and written input
- Have the learner do something with the input
i.e., Simple output, acting out - Keep the learner's processing strategies in mind
3. Structured output
3.1 Production/output
- Access: Retrieving the form, related to accuracy (correctness) and fluency (ease and speed)
- Monitoring: Editing one's speech
- Production strategies: String/put the forms and words together
3.2 Structured output
- Exchange of unknown information
- Access/use a particular form
3.3 Some structured output activities
- Comparing notes with someone else
- Taking notes, then writing a paragraph about what was said
- Making a list of follow-up questions and interviewing a partner to get the new information
- Filling out a grid or chart based on what was said
- Signing something
- Indicating agreement or disagreement
- Determining veracity of the statement
- Responding using any of several scales
- Drawing something
- Answering a question
- Example: https://chatgpt.com/share/67084060-25e8-800d-8bbc-da312558a2df
4. Teaching grammar
- Focus on form and meaning
- Error correction
- Explicit grammar instruction
- Assessing grammar proficiency